Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
Tags
- GPIO
- 리눅스
- QEMU
- avr-gcc
- vscode
- Visual Studio Code
- 라즈베리파이
- C++
- AVR
- 회로
- Linux
- raspberrypi
- atmel
- yocto
- c#
- 아두이노
- UART
- STM32
- nucleo
- 디버깅
- buildroot
- bare metal
- esp32
- Visual Studio
- Debug
- WPF
- Arduino
- Raspberry
- Debugging
- AArch64
Archives
- Today
- Total
임베디드를 좋아하는 조금 특이한 개발자?
pytorch를 통한 xor 게이트 학습 본문
예제 코드 : https://github.com/MainForm/xorNet
코딩을 처음 시작할때 "hello world"를 출력하는 것처럼 딥 러닝을 학습할 때 가장 처음으로 접하는 것이 XOR를 학습하는 것이라고 생각합니다. 기본적인 AND 연산이나 OR 연산의 경우 간단히 직선으로 구분하여 문제를 해결 가능합니다.
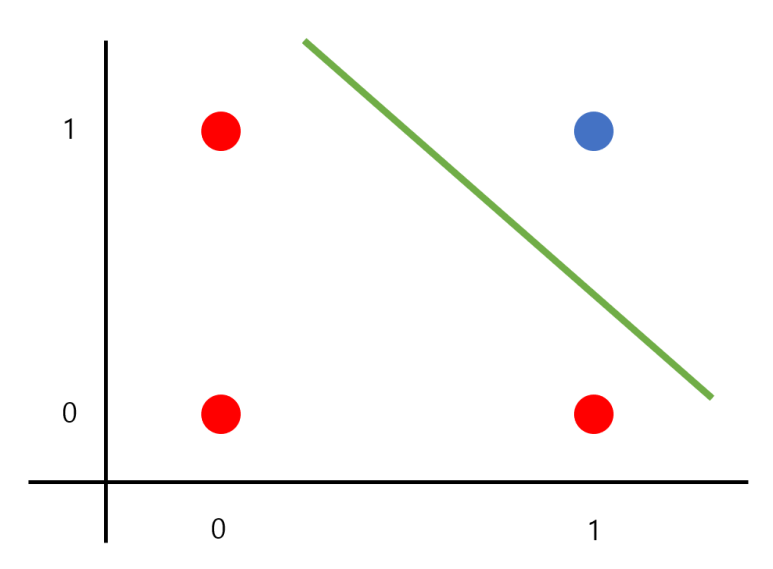
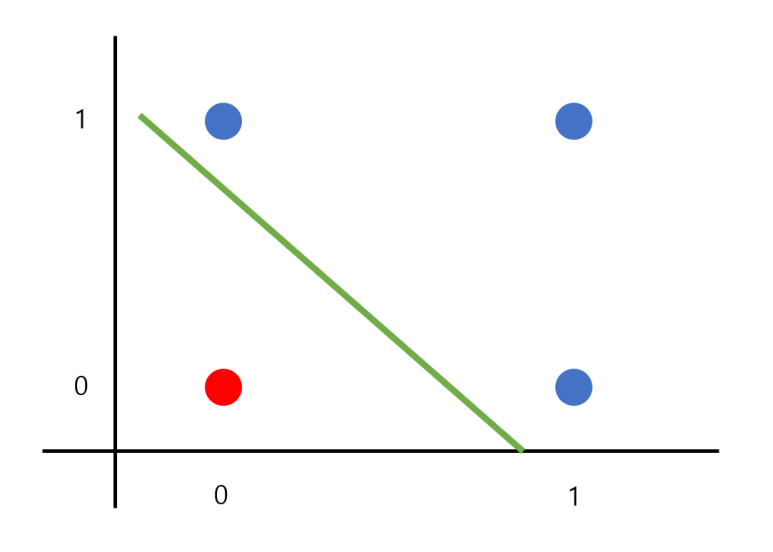
하지만 XOR의 경우에는 단순한 직선으로는 문제를 해결하지 못하고 곡선을 통해 문제를 해결하여야 합니다.
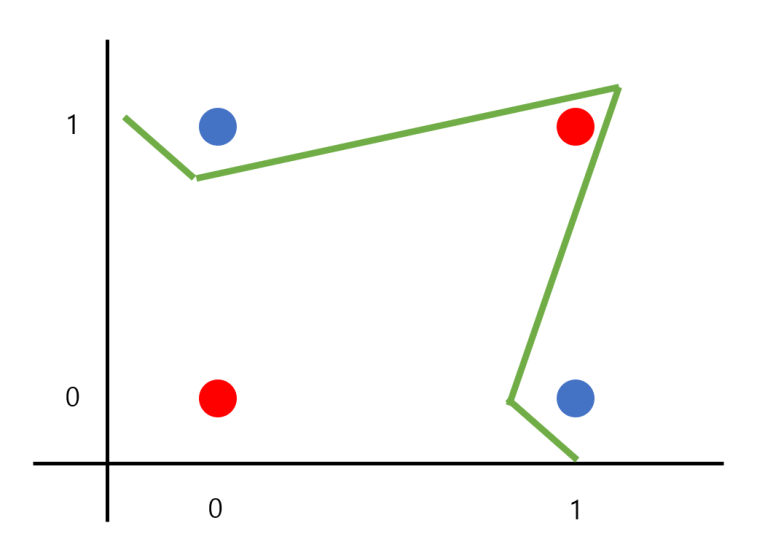
코딩의 순서로 Dataset를 만들고 Model를 만들고 나서 학습을 진행하도록 하겠습니다.
Dataset.py
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from random import randint
class xorDataSet(Dataset):
def __init__(self ,size=100000):
answer = [
#input answer
([0.,0.], 0.),
([0.,1.], 1.),
([1.,0.], 1.),
([1.,1.], 0.)
]
self.data = []
for _ in range(size):
self.data.append(answer[randint(0,len(answer) - 1)])
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
return torch.tensor(self.data[idx][0]), torch.tensor([self.data[idx][1]])
Model.py
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class xorNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(xorNet,self).__init__()
self.layer1 = nn.Linear(2,4)
self.layer2 = nn.Linear(4,1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.layer1(x)
x = F.sigmoid(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
return생성자에서 기본적인 Layer를 설계한후 forward() 맴버함수에서 학습 과정을 설계합니다.
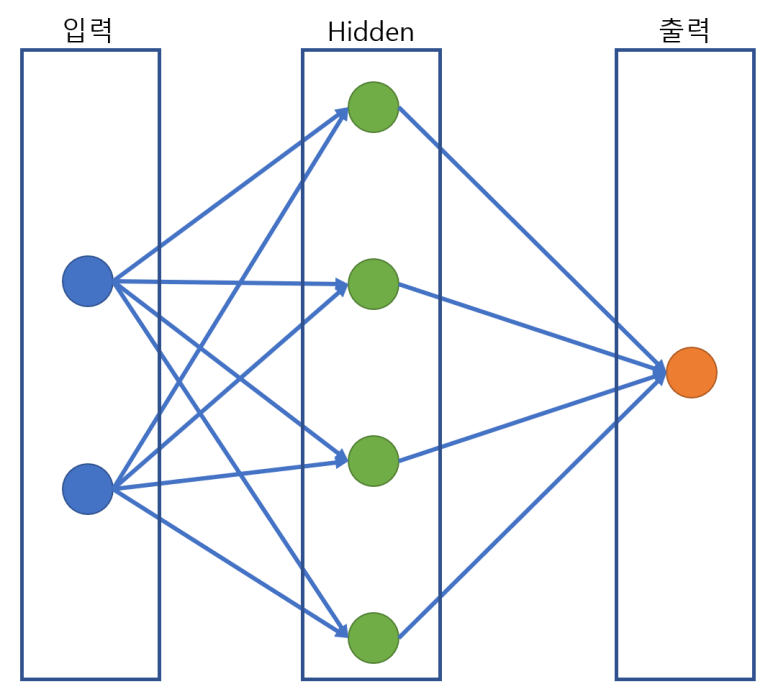
XOR의 경우 크게 어려운 문제가 아니기 때문에 레이어를 크게 쌓지 않았습니다. 또 결과의 범위가 0~1 사이 이기때문에 Sigmoid를 사용하였습니다.
Train.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from dataset import xorDataSet
from model import xorNet
# CUDA사용 가능 여부 확인
if torch.cuda.is_available() == True:
DEVICE = torch.device('cuda')
else:
DEVICE = torch.device('cpu')
BATCH_SIZE = 32
EPOCH_SIZE = 10
if __name__ == '__main__':
dataset = xorDataSet()
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset=dataset,batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,shuffle=True)
model = xorNet().to(DEVICE)
#optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(),lr = 0.1,momentum=0.5)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(),lr = 0.02)
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
for Epoch_idx in range(EPOCH_SIZE):
print(f'{Epoch_idx} : ')
model.train()
for idx, (input,answer) in enumerate(dataloader):
input = input.to(DEVICE)
answer = answer.to(DEVICE)
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(input)
loss = criterion(output,answer)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if idx % 100 == 0:
print(f'{idx * len(input)} / {len(dataloader.dataset)} losss : {loss.item()}')'DeepLearning > pyTorch' 카테고리의 다른 글
| torchvision.models에 있는 MobileNet V3 사용법 (0) | 2023.01.12 |
|---|

